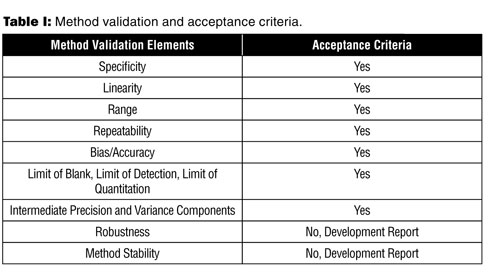
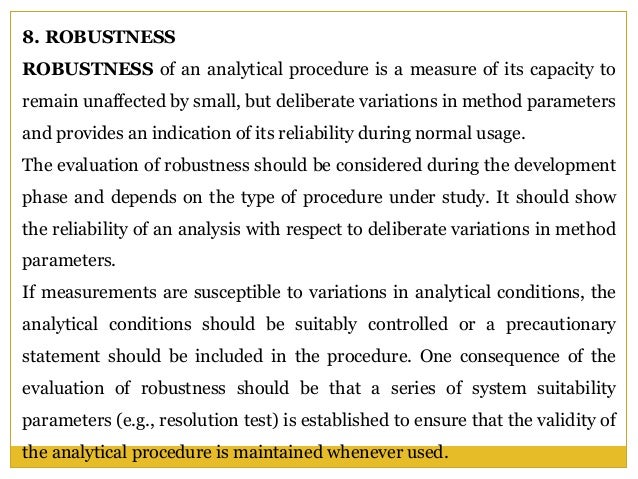
Meaning Of Robustness In Method Of Validation
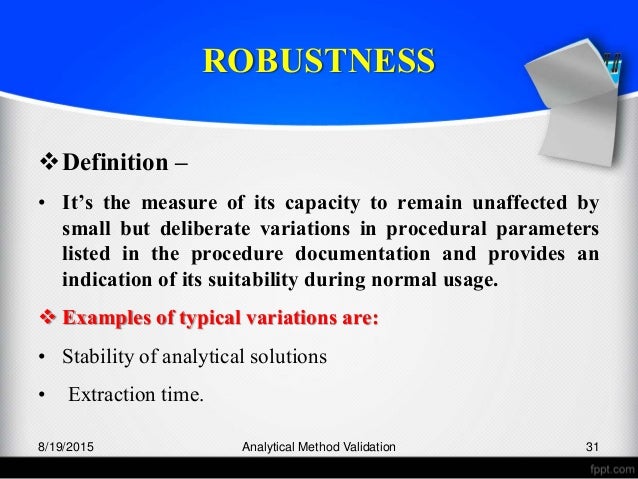
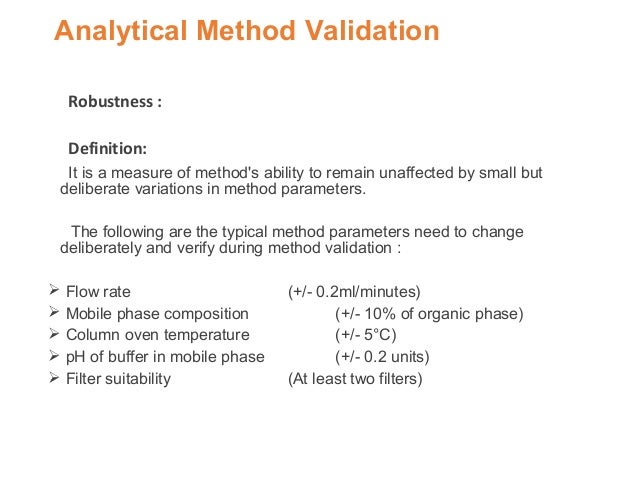
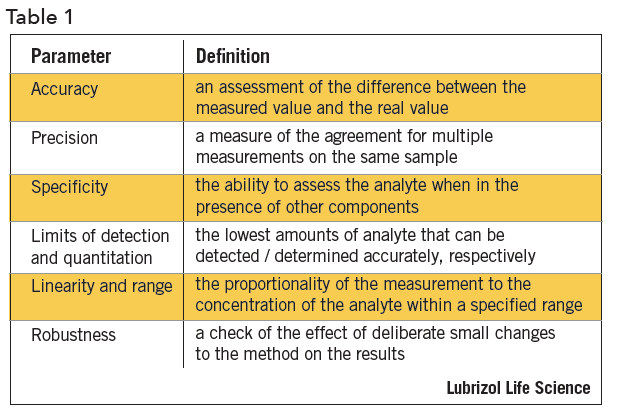
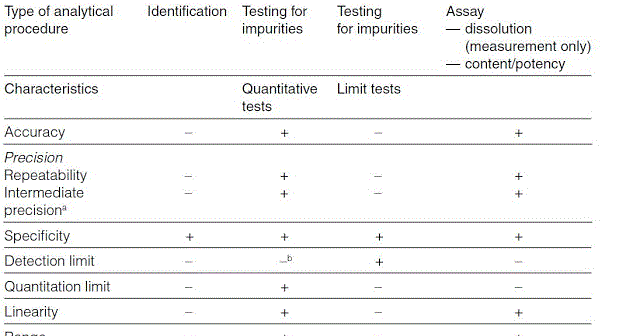
In the usp the robustness of an analytical procedure is defined as a measure of its capacity to remain unaffected by small but deliberate variations in method parameters and provides an indication of its reliability in normal usage.

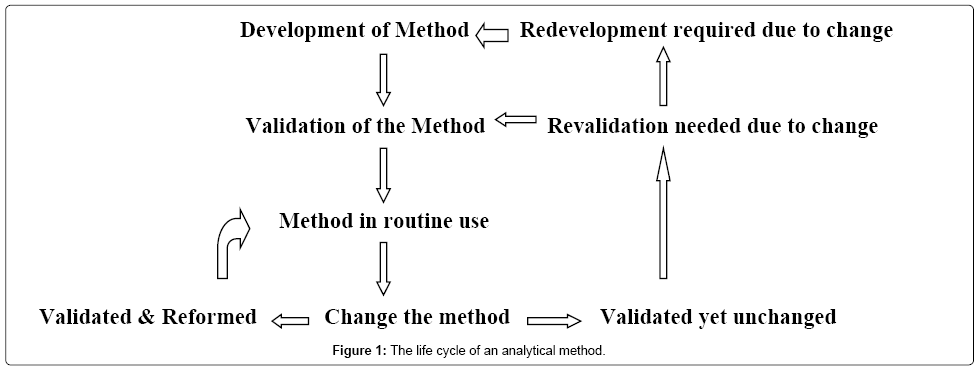
Meaning of robustness in method of validation. Robustness is the evaluation of an analytical method wherein the results obtained are found to be reliable even when performed in a slightly varied condition. In computer science robustness is the ability of a computer system to cope with errors during execution and cope with erroneous input. Usually we deliberately make changes in the method parameters to see if the method can still generate valid data. Robustness data obtained during a methods development can be submitted in support of the validation of a method.
Robustness traditionally has not been considered as a validation parameter in the strictest sense because usually it is investigated during method development once the method is at least partially optimized. Robustness can encompass many areas of computer science such as robust programming robust machine learning and robust security networkformal techniques such as fuzz testing are essential to showing robustness since this type of testing involves invalid. A robustness test is designed to show the reliability of a method response as different parameters are varied. In this part of the course the robustness and ruggedness are introduced and explained.
In this article we will address the same question through the parameter called robustness which can be evaluated during method validation if not yet done earlier eg. The purpose of a robustness study is to find out as much as possible about potential issues with a new analytical method and thus how it will perform in routine use. Robustness is not only an indicator of good practice in method development but also a regulatory requirement.